How Far Is The Star

The Nearest Neighbor Star
About the Paradigm
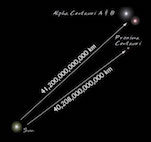
The image on the preceding page was created to demonstrate that Alpha Centauri is not a star, merely really a star system. Of the three stars in the system, the dimmest - chosen Proxima Centauri - is actually the nearest star to the Sun. The two bright stars, chosen Alpha Centauri A and B class a close binary system; they are separated past only 23 times the Globe - Sun distance. This is slightly greater than the distance betwixt Uranus and the Sun.
The Alpha Centauri system is not visible from much of the northern hemisphere. The below image shows this star system and other objects near it in the heaven.

Prototype Credit for Blastoff Centauri photo: Copyright Akira Fujii / David Malin Images.
Distance Information
Proxima Centauri, the closest star to our own, is still 40,208,000,000,000 km abroad. (Or about 268,770 AU.) When nosotros talk about the distances to the stars, we no longer employ the AU, or Astronomical Unit; unremarkably, the lite yr is used. A light twelvemonth is the distance light travels in 1 year - information technology is equal to nine.461 ten x12 km. Blastoff Centauri A & B are roughly four.35 calorie-free years away from usa. Proxima Centauri is slightly closer at iv.25 light years.
How Do We Calculate Distances of This Magnitude?
The methods astronomers use to mensurate distances to the stars are pieces of fundamental and agile work in astronomy with important implications for how nosotros understand the Universe around u.s.a..
I of the virtually accurate methods astronomers utilise to measure distances to stars is called parallax. If you concur your finger in front of your face and shut ane eye and expect with the other, and then switch optics, you'll see your finger seem to "shift " with respect to more distant objects behind it. This is because your eyes are separated from each other by a few inches - so each eye sees the finger in front of you from a slightly different angle. The amount your finger seems to shift is called its "parallax".
Astronomers can mensurate parallax by measuring the position of a nearby star very carefully with respect to more distant stars behind it, so measuring those positions once again six months later when the World is on the reverse side of its orbit. If the star is close enough to u.s., a measurable parallax will exist seen: the position of the star relative to the more distant groundwork stars will take shifted. The shift is tiny - less than an arcsecond even for the nearest star. (An arcsecond is 1/sixty of an arcminute, which is 1/60 of a degree.) (Imagine the Universe has more information on calculating parallax.)
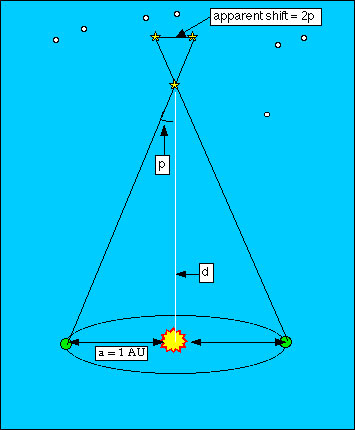
Image Credit: Imagine the Universe, NASA/GSFC
Why Are These Distances Important To Astronomers?
Stars are not actually stationary objects! The Galaxy is rotating, and the stars are in orbit effectually its middle. Non every star moves at the same rate - how fast they orbit tin depend on where the star is located within the Galaxy. Our Sunday, being fairly far from the Galactic Center, takes over 200 1000000 years to circumvolve the Milky way once. Some of the stars near us are moving faster than us, and some slower. Every bit Phil Plaitt, from Bad Astronomy says, "...like cars on a highway, stars continually pass each other as they orbit the Galaxy. They change positions, slowly, only measurably."

Image Credit: Frog Rock Observatory, public domain and copyright-free.
This animation by Frog Rock Observatory shows the move of Barnard's Star across the sky from 1985 to 2005. Barnard's Star is budgeted the Sun so rapidly that around 11,700 Advertisement, it volition be three.8 calorie-free years from the Sun - and thus the closest star to our ain! (Garcia-Sanchez, et al, 2001)
Travel Time
The Voyager 1 spacecraft is on an interstellar mission. It is traveling away from the Sun at a rate of 17.3 km/s. If Voyager were to travel to Proxima Centauri, at this rate, it would take over 73,000 years to arrive. If nosotros could travel at the speed of lite, an impossibility due to Special Relativity, information technology would notwithstanding take 4.22 years to arrive!
Why Can't We Travel Faster Than the Speed Of Calorie-free?
Co-ordinate to Special Relativity the mass of an object increases every bit its speed increases, and approaches infinity equally the object's speed approaches the speed of calorie-free. This means that it would take an infinite corporeality of free energy to accelerate an object to the speed of light.
At that place'south no central reason why we tin't get as close to the speed of light every bit we similar, provided we have enough energy. Just this is probably far in the future.
Back
How Far Is The Star,
Source: https://imagine.gsfc.nasa.gov/features/cosmic/nearest_star_info.html
Posted by: thompsoncutdomplad.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How Far Is The Star"
Post a Comment